"Our integration with the Google Nest smart thermostats through Aidoo Pro represents an unprecedented leap forward for our industry."
- Antonio Mediato, founder and CEO of Airzone.
Using AI in manufacturing has changed everything, setting new standards for how efficient, innovative, and environmentally friendly things can be made. Adopting AI technologies has become essential for makers to stay competitive in a market that is changing quickly. This is helping them reach new levels of quality and efficiency. It does this by improving quality control, predictive maintenance, and more.
This blog post briefly talks about 20 amazing ways AI is being used in the manufacturing industry. These examples show how this game-changing technology is changing every part of production and operations, and they also show how much room there is for growth and improvement in the sector.
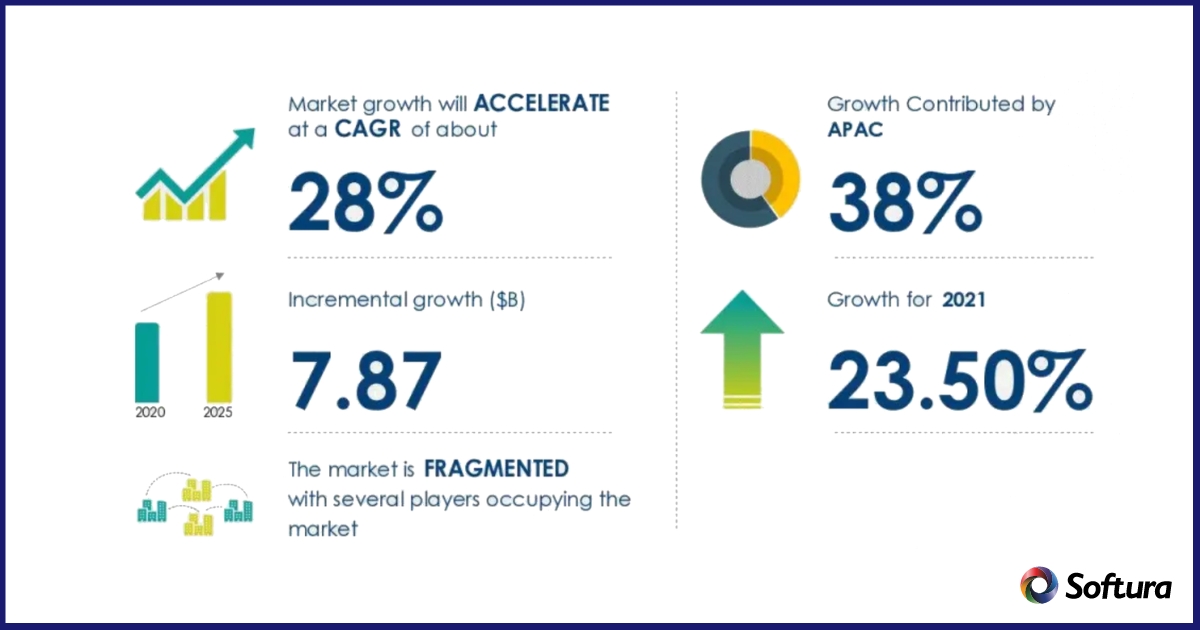
In the next few years, the world market for artificial intelligence (AI) in manufacturing is expected to grow very quickly, from USD 3.8 billion in 2023 to USD 68.36 billion by 2032. With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 33.5% from 2023 to 2032, this huge growth shows how important AI technologies are in changing the way things are made.
A Deloitte study report shows that 93% of companies see artificial intelligence as a key tool for driving growth in the industrial business. This shows how important AI is in the field.
Additionally, McKinsey predicts that AI's use in production will add nearly 19% to China's economic growth by 2030. This shows how powerful the technology is and how it could change the way the world's economies work.
People are realizing that AI can make operations more efficient, production methods more streamlined, and product quality much higher. This is driving the current growth in the AI in manufacturing market.
Because of this, additional resources are being put into AI technologies in many areas of industry, such as aircraft, household items, cars, and gadgets. AI technologies are becoming important for manufacturers who want to stay competitive in a fast-paced market as the industry moves toward Industry 4.0, which is made up of smart, interconnected systems.
"Our integration with the Google Nest smart thermostats through Aidoo Pro represents an unprecedented leap forward for our industry."
- Antonio Mediato, founder and CEO of Airzone.
AI in Predictive Maintenance
AI is used in predictive maintenance to understand impending equipment failures. This cuts down on downtime and maintenance costs. AI algorithms can find patterns in data from sensors and machines that point to possible problems. This lets maintenance be planned on time.
AI in Quality Control
AI makes quality control in manufacturing industry better by inspecting materials and products automatically. Machine learning models that have been trained on images of defects can quickly spot problems. It ensures the products meet quality standards while greatly cutting inspection times .
AI in Supply Chain Optimization
AI algorithms improve supply chain operations by figuring out the best delivery routes, predicting demand, and keeping track of the inventory levels. This lowers costs, raises fulfilment rates, and makes it easier to adapt to changes in the market.
AI in Inventory Management
AI-powered inventory management systems predict the demand of a product, keep track of inventory levels in real time, and automate the process of reordering. This cuts down on stock-outs and extra inventory, making the best use of storage space and capital.
AI in Production Planning and Scheduling
By analyzing various factors like machine availability, labor capacity, and material supply, AI tools help make more efficient production schedules. This leads to higher output, shorter lead times, and more operational flexibility.
AI in Machine Vision for Inspection
Machine vision systems that are powered by AI make it possible to visually inspect products and parts automatically. These systems can quickly and accurately find flaws in products, which improves quality and cuts down on the work needed for manual inspection.
AI in Robotics and Automation
AI gives robots the ability to do complicated tasks on their own and in new ways. In manufacturing, AI-powered robots can learn from their surroundings, get better over time, and work with people to make things more productive and efficient.
AI in Product Design and Development
AI speeds up the process of designing and making products by giving us insights from analysing data. It can mimic how a product works, suggest ways to make the design better, and even come up with new design ideas, which cuts down on the time it takes to get a product to market.
AI in Energy Management
AI makes manufacturing factories more energy-efficient by analyzing how energy is used and adjusting systems automatically for the best results. This helps cut down on energy use and the damage that manufacturing does to the environment.
AI in Worker Safety and Ergonomics
AI makes workers safer by monitoring the workplace and finding possible dangers. Wearable tech and sensors can let workers know about ergonomic risks, which can help keep them safer at work and lower the risk of injuries.
AI in Process Optimization
AI algorithms analyze production data to find places where manufacturing processes aren't working as well as they could and find bottlenecks. By making these processes more efficient, manufacturers can boost output, cut down on waste, and work better .
AI in Material Handling and Logistics
AI speeds up logistics and material handling by making warehouse operations more efficient and automating tasks like packing, transporting, and sorting materials. This makes the supply chain faster, more accurate, and more efficient.
AI in Custom Manufacturing and Personalization
By automating the design and production processes, AI lets companies make customized and personalized products. This method considers what each customer wants while still being efficient and low-cost.
AI in Predictive Analytics for Market Demand
AI-powered predictive analytics predicts what the market will demand, which helps manufacturers change how much they produce based on that. This keeps the right amount of inventory on hand, cuts down on waste, and makes it easier to adapt to changes in the market.
AI in Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability
AI tools maintain a close watch on and analyze data about the environment to find ways that manufacturing operations can have less of an effect on it. This includes making the best use of resources, cutting down on emissions, and getting better at managing waste.
AI in Cybersecurity for Manufacturing Systems
By finding threats and responding to them in real time, AI makes manufacturing systems safer. AI can find possible security holes by looking at system activities and network traffic. This keeps sensitive data and maintains operational integrity .
AI in Collaborative Robots (Cobots) Integration
AI makes cobots, which are made to work with people, better at doing tasks in a safer and more efficient way. Cobots can learn from human operators and adapt to changes in their environment - thanks to AI. This makes the workplace more social and productive.
AI in Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
AI improves additive manufacturing by guessing the best ways to print, checking the quality of the prints in real time, and changing settings to get the best results. This makes the products better and the production process run more smoothly.
AI in Digital Twin Technology
AI powers digital twins, which are virtual copies of physical systems that are used to test and study manufacturing processes. With this technology, manufacturers can test different scenarios, guess what will happen, and improve operations all without stopping production.
AI in Customer Service and Support
Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI offer customer service and support 24 hours a day, seven days a week. They answer questions, process orders, and make personalized suggestions. This makes the customer happier and speeds up the support process after the sale.
"By analyzing the data from our connected lights, devices and systems, our goal is to create additional value for our customers through data-enabled services that unlock new capabilities and experiences."
- Harsh Chitale, leader of Philips Lighting’s Professional Business.
The use cases discussed above are just a few examples of how Artificial Intelligence (AI) can positively impact the manufacturing industry.
To get the most out of AI in manufacturing, businesses need expert advice and custom solutions. Softura is at the front of this AI revolution. We offer customized AI development services and support to meet the specific needs of manufacturing companies that want to use AI technologies.
To learn more about any of these AI uses or think about implementing similar AI-based solutions in their own operations, get in touch with Softura right away.
"Our integration with the Google Nest smart thermostats through Aidoo Pro represents an unprecedented leap forward for our industry."
- Antonio Mediato, founder and CEO of Airzone.
Onboard Offshore Mobile App Developers
Develop Mobile application and integrate it into your business processes with Softura's dedicated offshore mobile app developers!