"Our integration with the Google Nest smart thermostats through Aidoo Pro represents an unprecedented leap forward for our industry."
- Antonio Mediato, founder and CEO of Airzone.
As the world increasingly turns its focus toward environmental sustainability, industries across all sectors must reimagine their processes and practices to minimize their ecological footprint.
The tech industry is no exception. Software development, while digital in nature, contributes significantly to carbon emissions, e-waste, and resource consumption. For developers and companies committed to eco-conscious practices, embracing sustainability is not just about reducing emissions but also creating long-term value through efficient, mindful development.
In this article, we explore sustainable practices for eco-conscious software development and the steps that developers and organizations can take to create more environmentally responsible products.

Writing energy-efficient code is one of the most effective ways to reduce the carbon footprint of a software product. Inefficient code can lead to increased energy consumption, both during development and when the software is in use by end users. By focusing on optimizing the performance of software, developers can reduce the amount of energy required for its execution, which in turn helps to conserve natural resources.
Reducing the complexity of software, especially for applications that run on a large scale or in the cloud, can significantly lower power consumption and extend the life of hardware.
"Our integration with the Google Nest smart thermostats through Aidoo Pro represents an unprecedented leap forward for our industry."
- Antonio Mediato, founder and CEO of Airzone.
A great example of energy-efficient coding practices in action is Google’s approach to data center optimization. Google has long focused on reducing the energy footprint of their operations, and this includes optimizing the software they run in their data centers.
In 2008, Google began using machine learning algorithms to optimize the operation of their data centers, adjusting cooling and other environmental variables in real-time to use less energy. However, they also made significant strides in improving the efficiency of the software running within these data centers.
For instance, they have worked to minimize the energy consumption of their Google Search engine and other services by writing more efficient code, reducing unnecessary computations, and enhancing algorithm efficiency.
Google has also adopted sustainable coding practices to ensure that their cloud-based infrastructure can scale efficiently without over-consuming power. The use of energy-efficient coding practices is one of the core components of their broader sustainability initiatives, which also include innovations like renewable energy-powered data centers.
Google's data centers now use approximately 50% less energy per unit of computing power than they did a decade ago, thanks to optimizations at both the hardware and software levels. Their energy efficiency efforts have contributed to their goal of running on 100% renewable energy.
"By analyzing the data from our connected lights, devices and systems, our goal is to create additional value for our customers through data-enabled services that unlock new capabilities and experiences."
- Harsh Chitale, leader of Philips Lighting’s Professional Business.
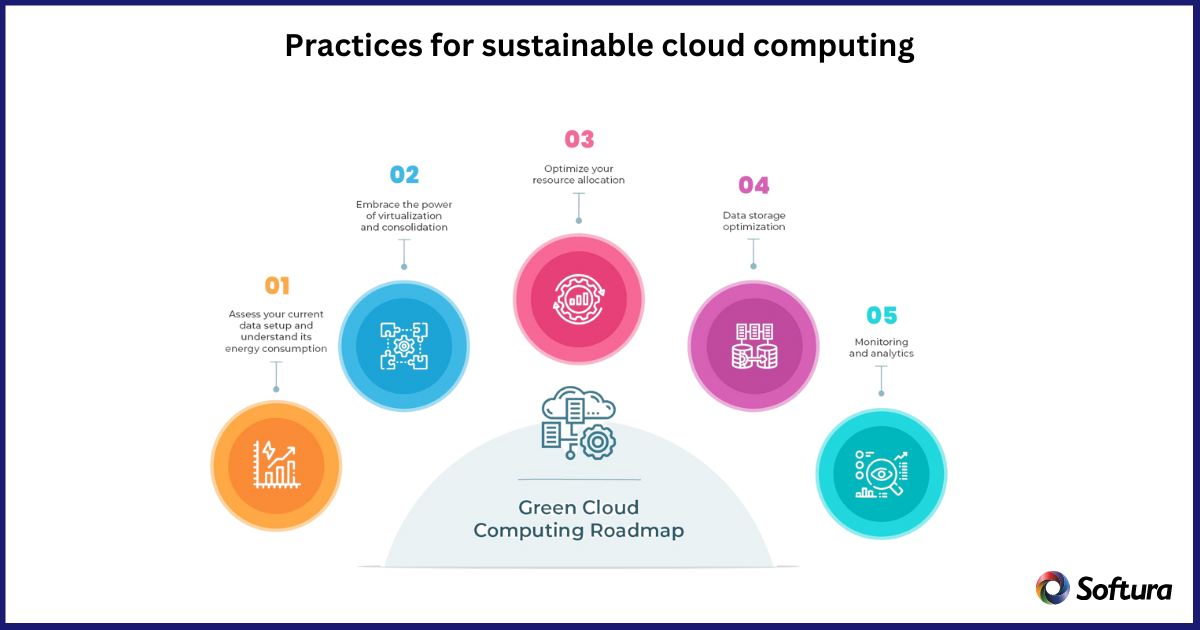
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and developers deploy software. However, with the growing reliance on data centers, the environmental impact of cloud computing has become a concern. The data centers that support cloud services consume vast amounts of energy and contribute to CO2 emissions, particularly if the energy comes from non-renewable sources.
When developing applications, think about how you can build them to be resource-efficient from the ground up. The more you can minimize the number of resources needed for an application to run, the less energy will be consumed overall.
Build Software That Respects the Planet
Drive innovation while cutting emissions with energy-efficient code, green cloud practices, and sustainable lifecycle management.
A real-life case illustrating cloud sustainability and resource optimization is Amazon Web Services (AWS). AWS has committed to powering its global infrastructure with 100% renewable energy by 2025. To achieve this, AWS is investing in large-scale renewable energy projects such as solar and wind farms and has implemented advanced energy efficiency technologies in its data centers.
These include liquid cooling and AI-based load balancing which improve energy efficiency by up to 40%. AWS also promotes cloud resource optimization practices like right-sizing workloads, auto-scaling, and serverless architectures to avoid unnecessary energy consumption from over-provisioning.
One notable example is the use of AWS Lambda for serverless computing, which automatically scales resources on demand and prevents idle server capacity from wasting power. This results in significant energy savings compared to always-on servers. Additionally, AWS encourages customers to optimize data storage by using tiered storage options, only using high-performance storage when needed, further reducing energy use from storage services.
This combination of sourcing renewable energy and optimizing resource usage exemplifies how cloud providers and enterprises can drastically reduce the carbon footprint of cloud computing while maintaining performance and flexibility.
The software development lifecycle (SDLC) involves various stages: planning, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Sustainable practices should be integrated into each of these stages to reduce waste, optimize resource use, and minimize environmental impact.
A sustainable SDLC not only helps the environment but can also lead to cost savings for businesses, as more efficient processes reduce unnecessary expenditures and resources.
While software development can be optimized for sustainability, the hardware that runs the software is just as crucial. The rapid pace of technological advancement often leads to the creation of e-waste ie., electronic products that are discarded, often improperly, at the end of their life cycles. E-waste poses significant environmental risks, as it contains toxic materials that can leach into the soil and water supply if not properly recycled.
By adopting practices that extend the lifespan of hardware and prioritize efficient resource usage, software development can play a significant role in reducing e-waste.
A real-life scenario for e-waste management and sustainable hardware choices can be seen in Microsoft's hardware and cloud sustainability initiatives. Microsoft emphasizes using energy-efficient, longer-lasting hardware and promotes repair over replacement to minimize e-waste. For example, the Surface product line is designed with repairability in mind, with components like batteries and displays that can be replaced to extend device life. Microsoft also works with certified e-waste recyclers to ensure safe disposal of old hardware.
Moreover, Microsoft encourages moving development and computing workloads to Microsoft Azure, their cloud platform, which is powered increasingly by renewable energy, thus reducing customers’ dependence on frequent hardware upgrades. Azure data centers implement advanced cooling and energy-saving technologies, and the company aims to be carbon negative by 2030.
These efforts showcase a sustainable hardware life cycle approach that includes:
This strategy reduces overall electronic waste and lowers the carbon footprint of both hardware manufacturing and usage.
Creating an eco-conscious culture within a development team or organization is essential for ensuring that sustainable practices are consistently applied. By fostering an environment where sustainability is a priority, organizations can empower developers to take ownership of their contributions to the planet's health.
Developers are key players in making the tech industry more sustainable. By nurturing a culture that values environmental responsibility, organizations can create meaningful change both in the industry and in society at large.
Sustainable software development is crucial for reducing the tech industry's environmental impact. By adopting energy-efficient coding practices, optimizing cloud infrastructure, and using green hosting, developers can minimize their software's carbon footprint. Designing for resource conservation, scalability, and longevity helps ensure that applications remain eco-friendly throughout their lifecycle.
Incorporating these practices not only benefits the planet but also improves performance and reduces operational costs.
At Softura, we’re committed to building eco-conscious software solutions that prioritize sustainability while driving innovation. Let’s work together to create a greener future.
Partner for Eco-Conscious Development
From cloud optimization to e-waste reduction, Softura helps enterprises align technology with sustainability goals without slowing delivery.